人肝癌细胞,Hep G2 [HEPG2],SHMCC E00311返回上一页
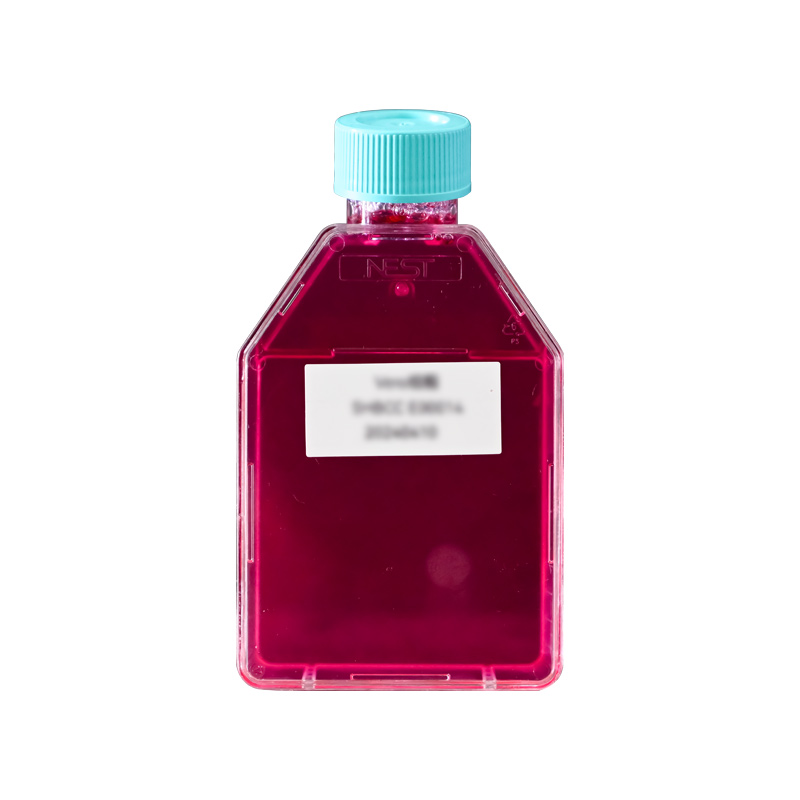

人肝癌细胞,Hep G2 [HEPG2],SHMCC E00311
菌株编号:SHMCC E00311
中文名称:人肝癌细胞,Hep G2 [HEPG2],SHMCC E00311
拉丁名称:
价格:¥1400
状态:咨询客服
下载:
产品介绍
平台资源号:
保藏编号:SHMCC E00311
中文名称:人肝癌细胞,Hep G2 [HEPG2],SHMCC E00311
拉丁名称:
模式菌株:
其它保藏中心编号:
来源历史:肝脏
收藏时间:
参考用途:动物种类:人组织来源:肝脏形态:上皮样,贴壁生长性别:男性,15岁细胞描述:人肝癌细胞Hep G2 [HEPG2]来源于一个15岁的白人男性肝癌患者。该细胞表达3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰还原酶(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA)和肝三酰甘油脂肪(hepatic triglyceride lipase)活性。此细胞不携带乙肝病毒基因组(Hepatitis B virus)。模式染色体数为55(50-60不等)。在免疫抑制小鼠中不致瘤
生物危害程度:
致病对象:
培养温度:人肝癌细胞 Hep G2完全培养液 配方(100 ml):MEM (Invitrogen,11090081) 87 mlFBS (Gibco) 10 mlGlutamax(invitrogen 35050061) 1 mlNon-essential Amino Acids, 100x (Invitrogen, 11140050) 1 mlSodium Pyruvate 100 mM Solution(invitrogen 1
需氧类型:气相:空气,95%;二氧化碳,5%。
提供方式:T25培养瓶,干冰冻存管(额外+150元)
保存温度:液氮
培养条件
人肝癌细胞 Hep G2完全培养液 配方(100 ml):MEM (Invitrogen,11090081) 87 mlFBS (Gibco) 10 mlGlutamax(invitrogen 35050061) 1 mlNon-essential Amino Acids, 100x (Invitrogen, 11140050) 1 mlSodium Pyruvate 100 mM Solution(invitrogen 11360070) 1 ml参考传代周期:4-6天参考传代比例:1:3参考换液频率:传代时换液冻存液:完全培养液95%,DMSO 5%细胞状态:贴壁生长气相:空气,95%;二氧化碳,5%。温度:37摄氏度。备注:Hep G2 [HEPG2]对培养条件要求较严格,特别是pH值和血清质量,否则可能影响细胞凝集数量,应使用高质量低内毒素,未灭火的胎牛血清,可以帮助圆形的细胞丛簇更好的贴壁及形成单层细胞。细胞内容易有空泡,特别是在融合时。
参考文献
Knowles BB, et al. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science 209: 497-499, 1980. PubMed: 6248960Knowles BB, Aden DP. Human hepatoma derived cell line, process for preparation thereof, and uses therefor. US Patent 4,393,133 dated Jul 12 1983Schardt C, et al. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor II receptors in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Exp. Cell Res. 204: 22-29, 1993. PubMed: 8380141Aden DP, et al. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma- derived cell line. Nature 282: 615-616, 1979. PubMed: 233137Busch SJ, et al. Differential regulation of hepatic triglyceride lipase and 3-hydroxy-3- methylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene expression in a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 22474-22479, 1990. PubMed: 2176219Darlington GJ, et al. Growth and hepatospecific gene expression of human hepatoma cells in a defined medium. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 23: 349-354, 1987. PubMed: 3034851Cuthbert C, et al. Regulation of human apolipoprotein A-I gene expression by gramoxone. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 14954-14960, 1997. PubMed: 9169468Deleersnyder V, et al. Formation of native hepatitis C virus glycoprotein complexes. J. Virol. 71: 697-704, 1997. PubMed:8985401Benn J, et al. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein induces transcription factor AP-1 by activation of extracellular signal-regulated and c-Jun N-terminal mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Virol. 70: 4978-4985, 1996. PubMed: 8764004Goodrum FD, et al. Adenovirus early region 4 34-kilodalton protein directs the nuclear localization of the early region 1B 55-kilodalton protein in primate cells. J. Virol. 70: 6323-6335, 1996. PubMed: 8709260Kolanus W, et al. alphaLbeta2 integrin/LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 induced by cytohesin-1 a cytoplasmic regulatory molecule. Cell 86: 233-242, 1996. PubMed: 8706128Lewis W, et al. Fialuridine and its metabolites inhibit DNA polymerase gamma at sites of multiple adjacent analog incorporation, decrease mtDNA abundance, and cause mitochondrial structural defects in cultured hepatoblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 3592-3597, 1996. PubMed: 8622980Jang SI, et al. Activator protein 1 activity is involved in the regulation of the cell type-specific expression from the proximal promoter of the human profilaggrin gene. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 24105-24114, 1996. PubMed: 8798649Roesler WJ, et al. The alpha-isoform of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein is required for mediating cAMP responsiveness of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase promoter in hepatoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 8068-8074, 1996. PubMed: 8626491Lee JH, et al. The proximal promoter of the human transglutaminase 3 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 4561-4568, 1996. PubMed: 8626812Lieber A, et al. Recombinant adenoviruses with large deletions geneerated by cre-mediated excision exhibit different biological properties compared with first-generation vectors in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 70: 8944-8960, 1996. PubMed: 8971024Dubuisson J, Rice CM. Hepatitis C virus glycoprotein folding: disulfide bond formation and association with calnexin. J. Virol. 70: 778-786, 1996. PubMed: 8551615Yamaguchi Y, et al. Biochemical characterization and intracellular localization of the Menkes disease protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 14030-14035, 1996. PubMed: 8943055Kounas MZ, et al. Cellular internalization and degradation of antithrombin III-thrombin, heparin cofactor II-thrombin, and alpha1-antitrypsin-trypsin complexes is mediated by the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 6523-6529, 1996. PubMed: 8626456Klemm DJ, et al. Adenovirus E1A proteins regulate phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription through multiple mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 8082-8088, 1996. PubMed: 8626493Wu X, et al. Demonstration of a physical interaction between microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and apolipoprotein B during the assembly of ApoB-containing lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 10277-10281, 1996. PubMed: 8626595Ostlund RE Jr., et al. A sterospecific myo-inositol/D-chiro-inositol transporter in HepG2 liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 10073-10078, 1996. PubMed: 8626564Knowles BB, Aden DP. Human hepatoma derived cell line, process for preparation thereof, and uses therefor. US Patent 4,393,133 dated Jul 12 1983

 021-59199805
021-59199805

 集团咨询服务号
集团咨询服务号




